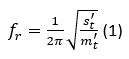Dynamic stiffness

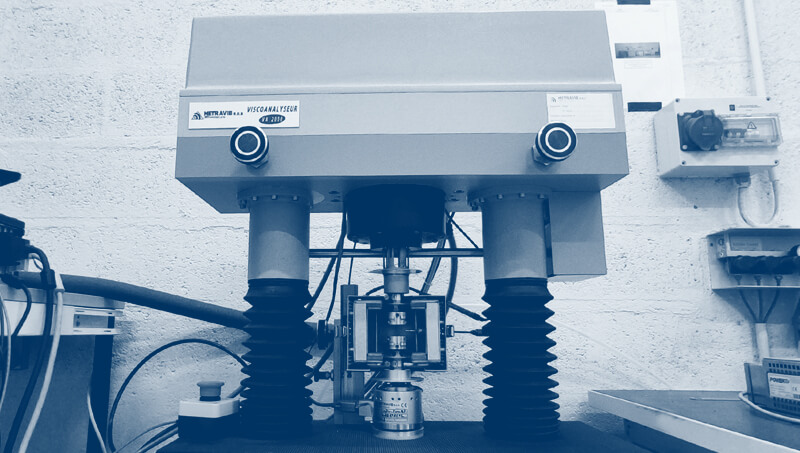
The CEVAA determines the dynamic stiffness of building materials to determine the elasticity of floors and their vibro-acoustic behavior.
Dynamic stiffness
In the construction sector, it is important to know the elasticity of floating floors and light floors. Indeed, this property determines the vibro-acoustic behavior of these systems, i.e. their performance to impact noise and walking noise.
For example, the elasticity of a screed on a glass wool depends directly on the elasticity of the material constituting the screed (for example, a mortar) and on the elasticity of the glass wool supporting the screed. In order to be representative of operational conditions, the elasticity of wool must be measured under load.
This characterization is called the measure of dynamic stiffness.
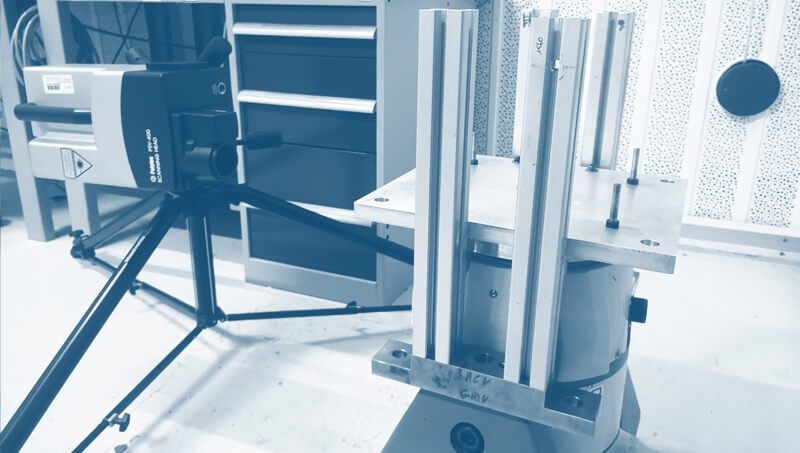
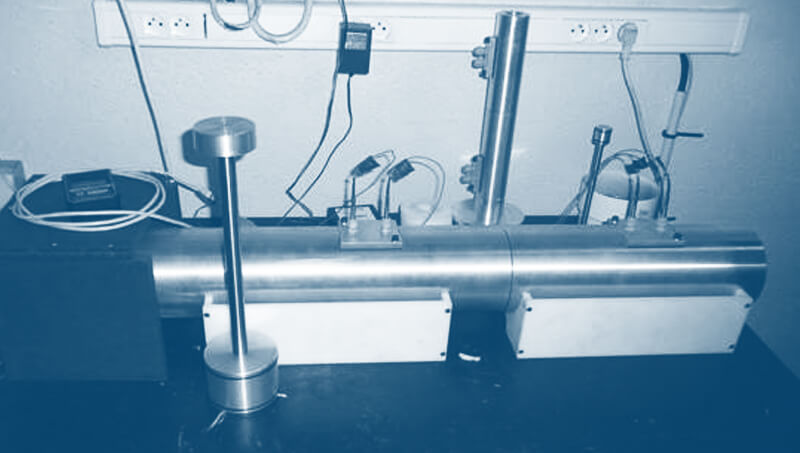
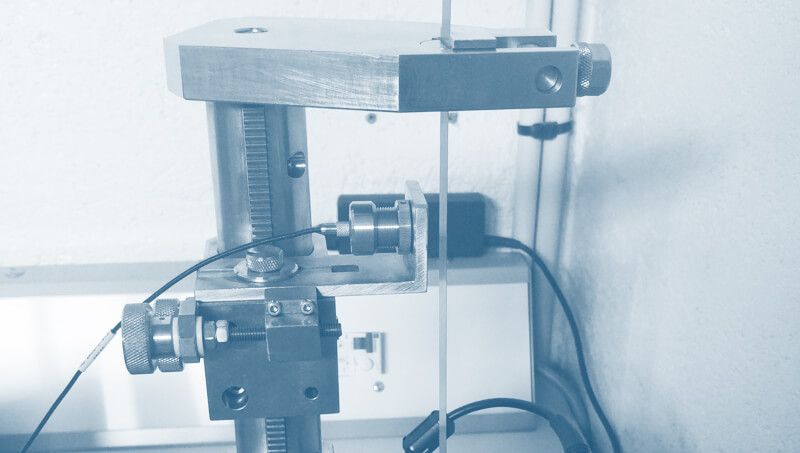
The CEVAA has a measurement bench dedicated to this characterization.
Dynamic stiffness calculation
The determination of the resonance frequency fr of the mass/spring/mass system makes it possible to obtain the apparent dynamic stiffness per unit area s’t of the specimen according to the equation:
With m’t the total mass per unit area used during the test.
The dynamic stiffness per unit area is expressed in MN/m3 and is equivalent to the sum of s’t, the apparent dynamic stiffness per unit area, and s’a, the dynamic stiffness per unit area of the trapped gas.
This formula is only valid in the case of poroelastic materials such as wool, foam or felt. In the case of solid materials, the dynamic stiffness per unit area is directly determined from equation (1).

Materials characterization benches
For more information, contact us to discuss technically on your needs!